What is Sake Made Of?
Sake is a traditional Japanese alcoholic beverage made from rice, water, koji mold, and yeast. Rice is the primary ingredient used in sake brewing. The rice must have a specific type of starch known as shinpaku, which is soft and low in protein, making it ideal for brewing sake. The rice used for sake brewing is different from table rice as it undergoes a polishing process to remove the outer layers of the grain, which contain unwanted fat and protein. Koji mold is a type of fungus that is made by inoculating steamed rice with koji spores. Koji mold breaks down the starch in the rice, creating sugar, which is essential for fermentation. The yeast is responsible for fermentation and converting sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The type of yeast used in the fermentation process can impact the flavor of sake. Water is crucial for sake fermentation and can affect the flavor of the final product. Soft water with low mineral content is the best water for brewing sake. There are also other additives used in sake brewing, such as acids, amino acids, and yeast nutrients, which impact the sake’s taste, aroma, and texture.
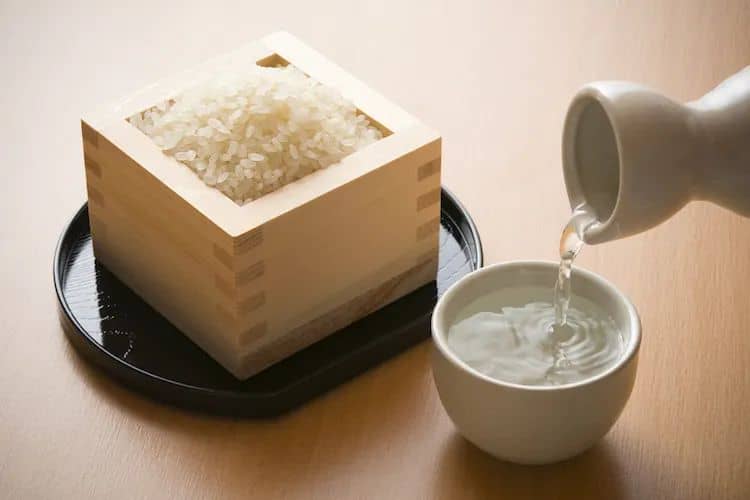

The Main Ingredient: Rice
Rice is the primary ingredient used in sake brewing. The rice must have a specific type of starch known as shinpaku. This type of rice is soft and low in protein, making it ideal for brewing sake. The rice used for sake brewing is different from table rice as it has undergone a polishing process. Rice polishing is the process of removing the outer layers of the rice grain, leaving only the starchy core. This process is essential because the outer layers contain unwanted fat and protein, which can affect the flavor and texture of the sake.
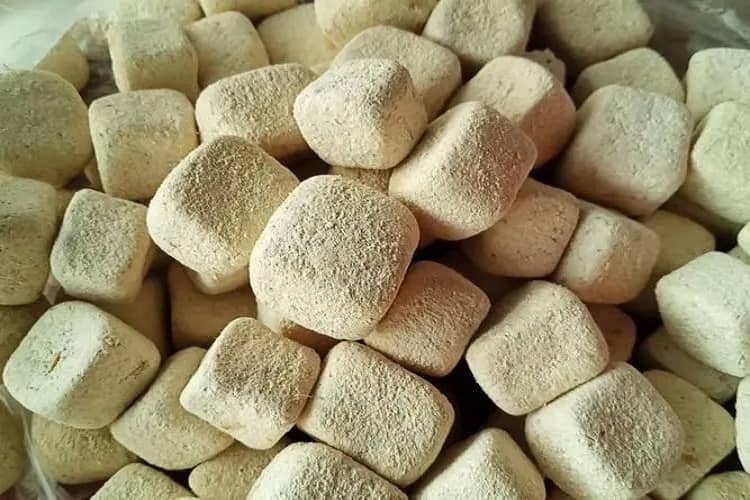

The Role of Koji Mold
Koji mold is a type of fungus that plays a crucial role in the sake-making process. Koji is made by inoculating steamed rice with koji spores. The koji mold breaks down the starch in the rice, creating sugar, which is essential for fermentation. Koji mold transforms the rice into koji, a magical ingredient that gives sake its unique flavor, aroma, and body. There are different types of koji mold, each with a different flavor profile and level of sweetness.
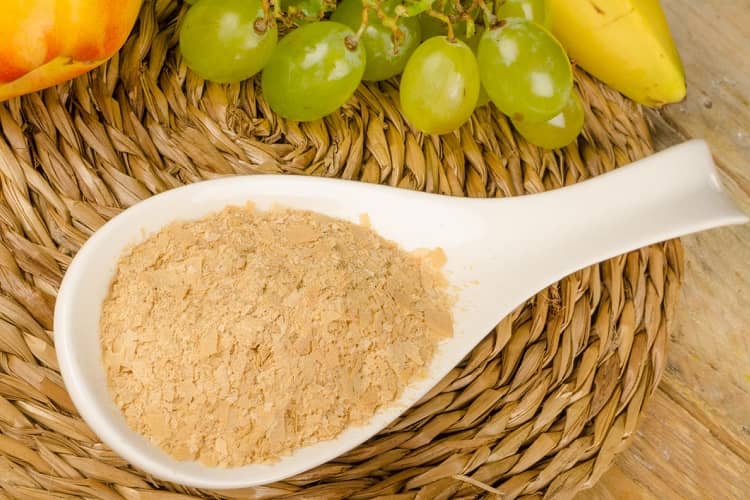

The Role of Yeast
Yeast is another essential ingredient in sake brewing. Yeast is responsible for fermentation, converting sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The type of yeast used in the fermentation process can impact the flavor of sake. Some yeast strains produce fruity, floral, and sweet flavors, while others create rich, earthy, and savory flavors. Brewers often choose different yeast strains or mixtures of yeast to create a unique and balanced taste.
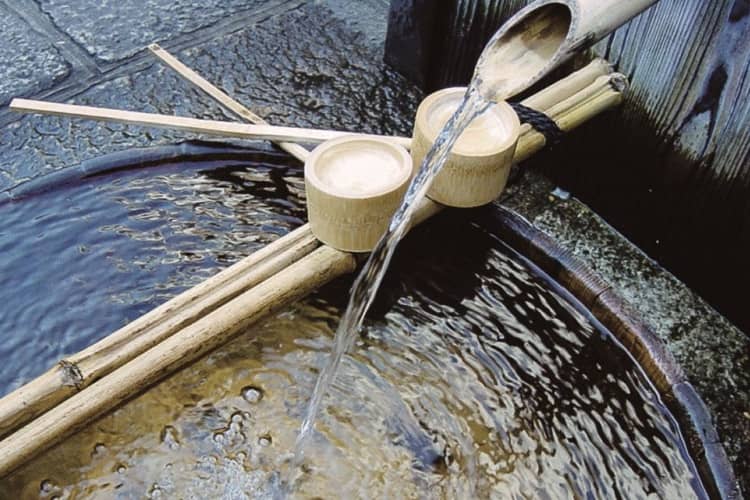

Water and Other Additives
Water is crucial for sake fermentation and can affect the final product’s taste. Soft water with low mineral content is the best water for brewing sake. Minerals in water can affect the flavor of sake and cause unwanted reactions during fermentation. There are other additives used in sake brewing, such as acids, amino acids, and yeast nutrients. These additives can impact the sake’s taste, aroma, and texture and require careful consideration during production.
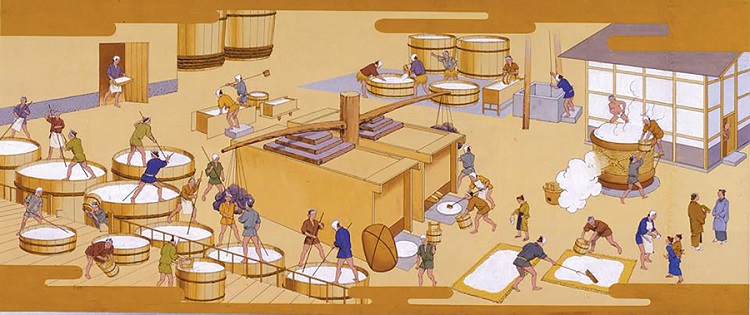
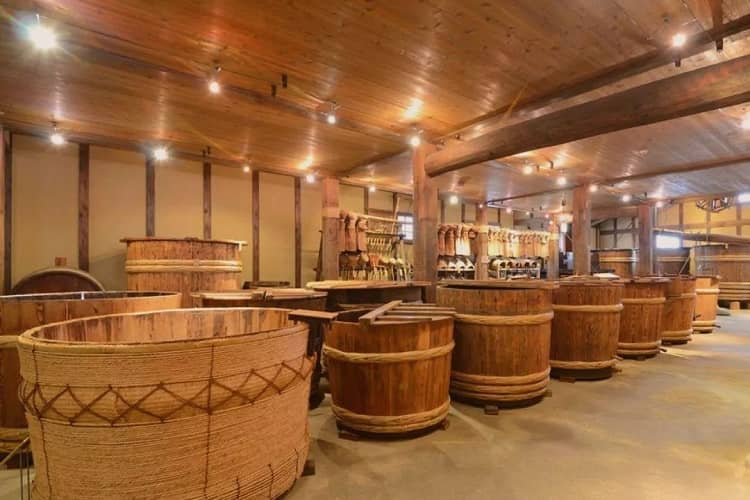
Methods of Production
There are two main methods of sake production: the traditional method and the modern method. The traditional method is the more labor-intensive and time-consuming process of sake brewing and involves the use of a wooden pressing machine. The modern method of brewing sake is more mechanical and uses machines for the process. The difference in production methods affects the final product’s flavor, texture, and aroma.

Conclusion
In conclusion, sake is a unique alcoholic beverage that requires expertly crafted methods and ingredients to create its distinct flavor. Understanding the role of rice, koji mold, yeast, water, and other additives in the sake-making process can help us appreciate the artistry and science behind this traditional Japanese beverage. As sake’s popularity continues to grow worldwide, it’s essential to retain the methods of traditional sake production while continuing to innovate and develop new techniques for the modern world.







